Equinor and RWE to develop hydrogen-fired power plants in Germany, Norway-to-Germany hydrogen pipeline
Green Car Congress
JANUARY 6, 2023
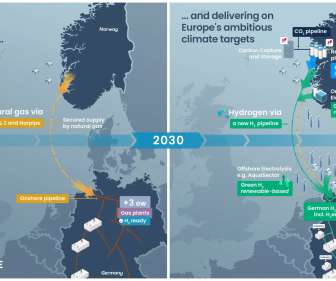
The partners aim to replace coal-fired power plants with hydrogen-ready gas-fired power plants in Germany, and to build production of low carbon and renewable hydrogen in Norway that will be exported through pipeline to Germany. Germany has an ambition to phase out all coal fired power plants by 2030.


































Let's personalize your content