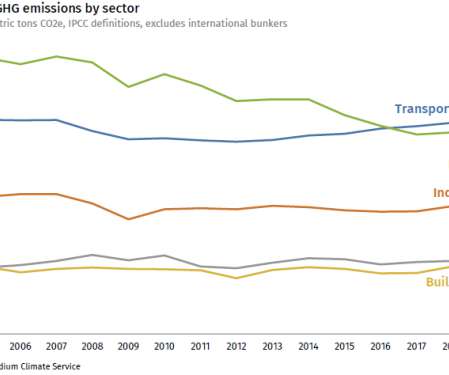
Rhodium Group estimates US GHG fell 2.1% in 2019, driven by coal decline
Green Car Congress
JANUARY 8, 2020
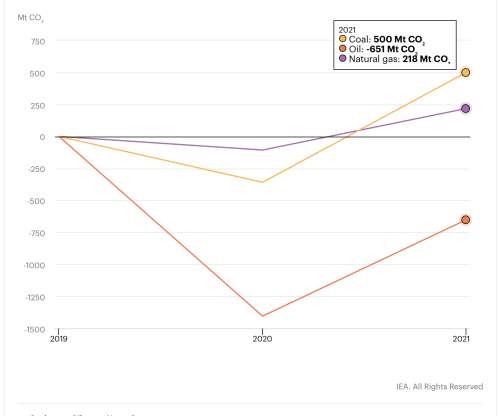
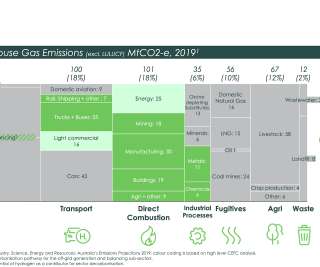
This decline was due almost entirely to a drop in coal consumption. Coal-fired power generation fell by a record 18% year-on-year to its lowest level since 1975. An increase in natural gas generation offset some of the climate gains from this coal decline, but overall power sector emissions still decreased by almost 10%.




































Let's personalize your content