UT El Paso-led team designs cactus-inspired low-cost, efficient water-splitting catalyst
Green Car Congress
MAY 16, 2023
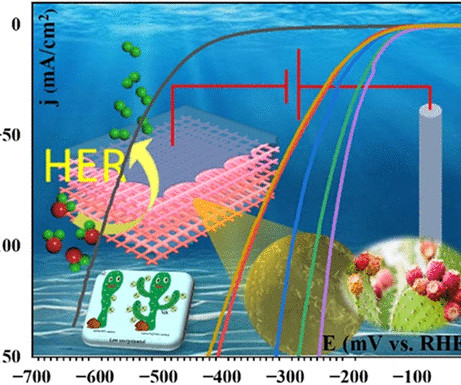
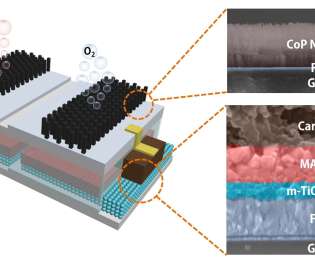
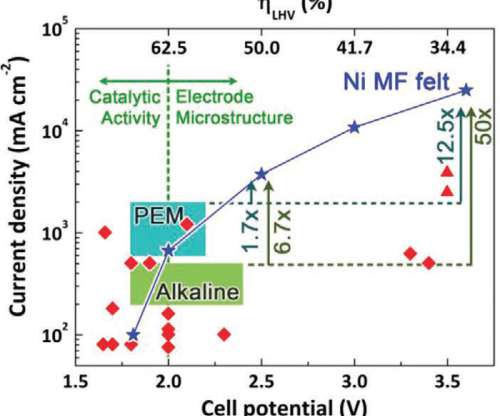
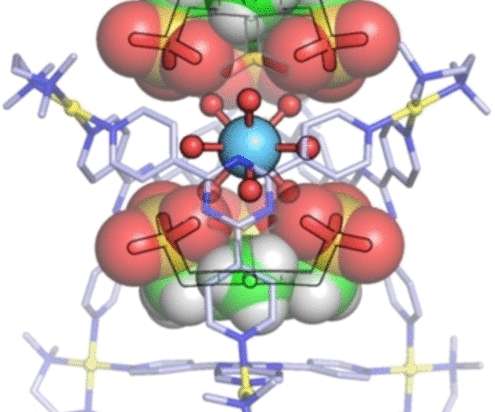
Researchers led by engineers at The University of Texas at El Paso (UTEP) have proposed a low-cost, cactus-inspired nickel-based material to help split water more cheaply and efficiently. Nickel, however, is not as quick and effective at breaking down water into hydrogen. And I started connecting it to our catalyst problem.




































Let's personalize your content