Veolia launches largest project to produce bio-methanol from pulp mill waste
Green Car Congress
APRIL 7, 2022
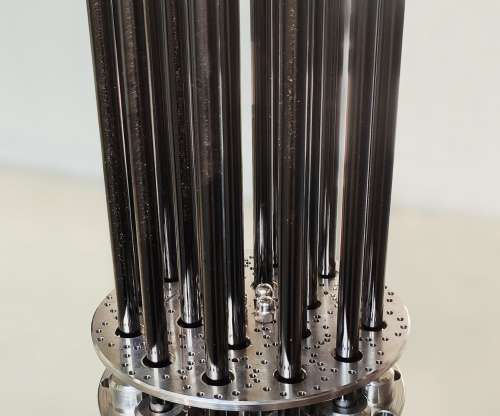
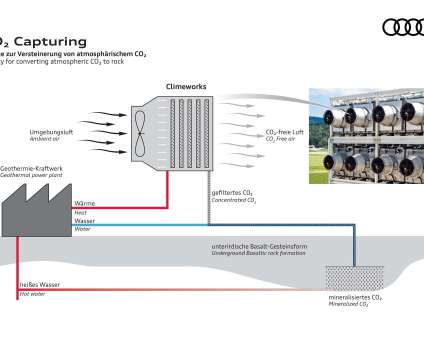
Using the A-Recovery+ concept from ANDRITZ, the plant has a capacity to produce 6.3 million liters of biomethanol which will be sold as a substitute for fossil-based methanol in the transport sector. Black liquor is the waste byproduct from the kraft pulping process after pulping is completed. Metsä Fibre’s Äänekoski plant.










































Let's personalize your content