How Safe Are EVs for Fleets?
Blink Charging
FEBRUARY 8, 2024
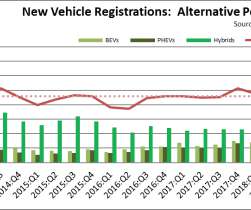
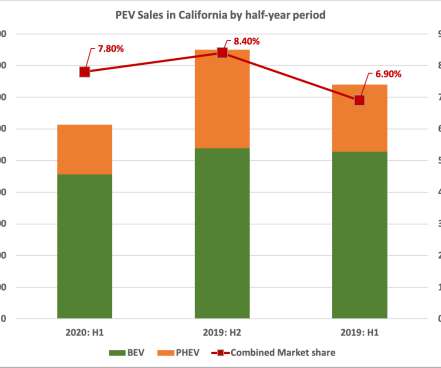
Many fleet owners and operators are interested in reducing operational and maintenance costs with electric vehicles (EVs), but they worry about vehicle safety. To meet these standards, vehicles must undergo an extensive, long-established testing process, regardless of whether the vehicle operates on gasoline or electricity.










































Let's personalize your content