Rice U team creates low-cost, high-efficiency integrated device for solar-driven water splitting; solar leaf
Green Car Congress
MAY 5, 2020
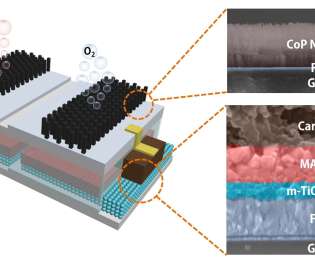
Rice University researchers have created an efficient, low-cost device that splits water to produce hydrogen fuel. The platform developed by the Brown School of Engineering lab of Rice materials scientist Jun Lou integrates catalytic electrodes and perovskite solar cells that, when triggered by sunlight, produce electricity.










































Let's personalize your content