HEI study links fossil fuel combustion with more than 1 million deaths globally
Green Car Congress
DECEMBER 15, 2021
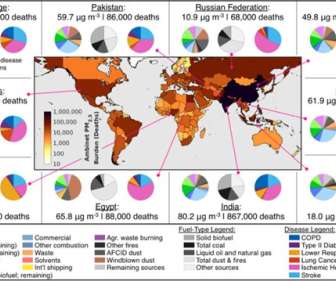
Fossil fuel combustion, a major source of air pollution, contributed to more than one million deaths globally in 2017, more than 27% of all deaths from outdoor fine particulate matter (PM 2.5 ), according to a new report published by the Health Effects Institute (HEI). According to HEI’s State of Global Air , PM 2.5




































Let's personalize your content