Electric vs. Gasoline Cars: Uncovering the Real Climate Savior
The Truth About Cars
FEBRUARY 23, 2024
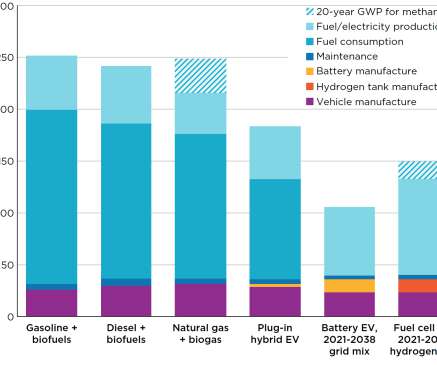
Photo credit: Nick Starichenko / Shutterstock.com Contrary to common misconceptions , electric vehicles (EVs) generally have a smaller carbon footprint compared to traditional gasoline cars. This advantage remains true even when considering the electricity utilized for charging EVs.









































Let's personalize your content