BloombergNEF: clean energy investment in developing nations slumps as financing in China slows; coal burn surges to record high
Green Car Congress
NOVEMBER 26, 2019
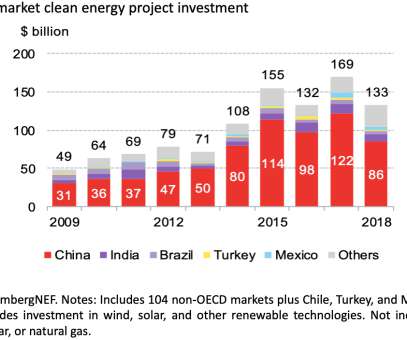
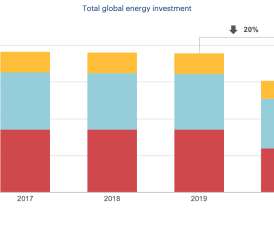
New investment in wind, solar, and other clean energy projects in developing nations dropped sharply in 2018, largely due to a slowdown in China. This is due to wind and solar projects generating only when natural resources are available while oil, coal, and gas plants can potentially produce around the clock.








































Let's personalize your content