EIA: CO2 emissions from US power sector have declined 28% since 2005
Green Car Congress
DECEMBER 24, 2018
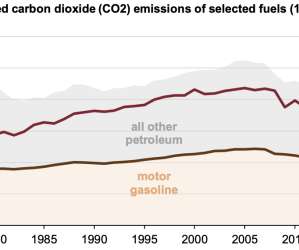
US electric power sector CO 2 emissions have declined 28% since 2005 because of slower electricity demand growth and changes in the mix of fuels used to generate electricity, according to the US Energy Information Administration (EIA). If electricity demand had continued to increase at the average rate from 1996 to 2005 (1.9%
































Let's personalize your content