PNNL biocrude-to-diesel demo passes 2,000-hour catalyst stability milestone
Green Car Congress
MARCH 26, 2021
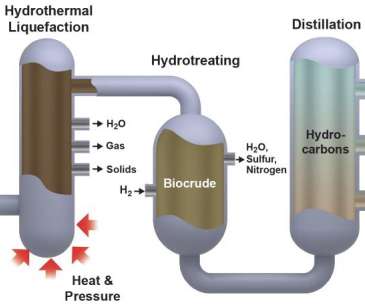
The biocrude oil came from many different sources, including wastewater sludge from Detroit, and food waste collected from prison and an army base. The research showed that essentially any biocrude, regardless of wet-waste sources, could be used in the process and the catalyst remained robust during the entire run.


































Let's personalize your content