Study finds methane emissions from coal mines ~50% higher than previously thought
Green Car Congress
FEBRUARY 1, 2021
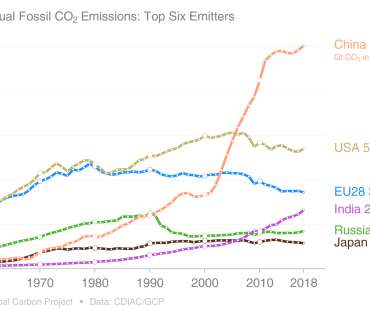
The amount of methane released into the atmosphere as a result of coal mining is likely approximately 50% higher than previously estimated, according to research presented at the recent annual meeting of the American Geophysical Union. The study is one of the first to account for methane leaking from old, abandoned mines.






































Let's personalize your content