MIT engineers create 2D polymer that self-assembles into sheets
Green Car Congress
FEBRUARY 3, 2022
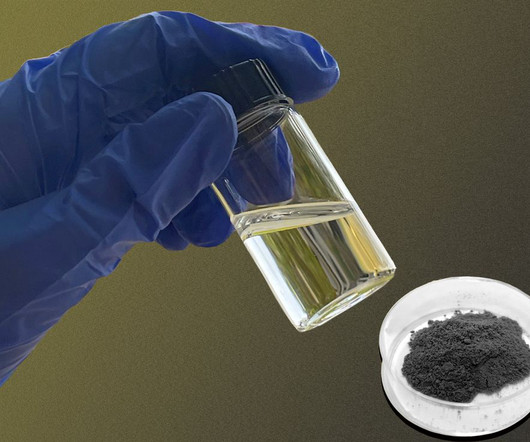
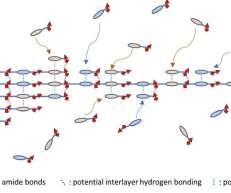
Using a novel polymerization process, MIT chemical engineers have created a new two-dimensional polymer that self-assembles into sheets, unlike all other polymers which form one-dimensional chains. Dubbs Professor of Chemical Engineering at MIT and the senior author of the new study. —Michael Strano.



































Let's personalize your content