New catalyst opens door to CO2 capture in coal-to-liquids process
Green Car Congress
OCTOBER 14, 2018
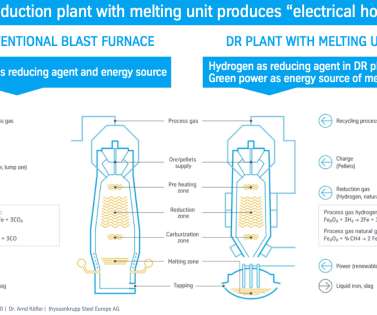
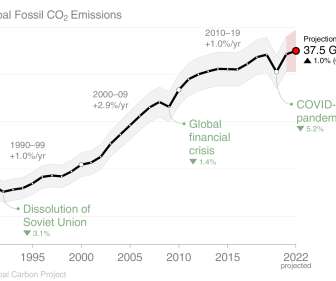
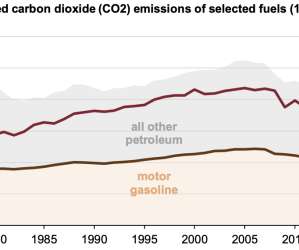
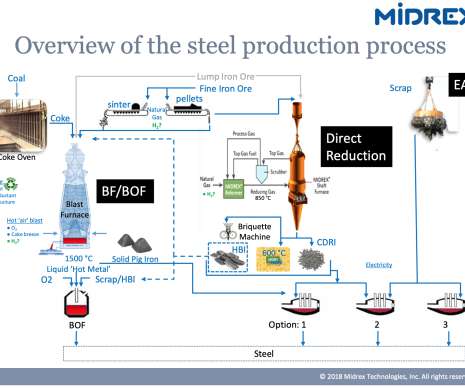
World energy consumption projections expect coal to stay one of the world’s main energy sources in the coming decades, and a growing share of it will be used in CT—the conversion of coal to liquid fuels (CTL). By 2020, CTL is expected to account for 15% of the coal use in China. —Wang et al.



































Let's personalize your content