Utility solar dethrones coal as the cheapest power source in Asia
Baua Electric
FEBRUARY 29, 2024
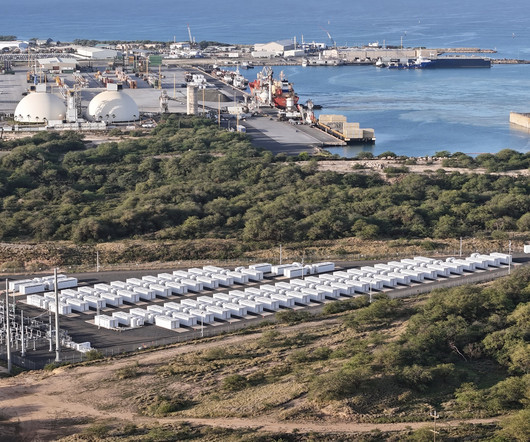
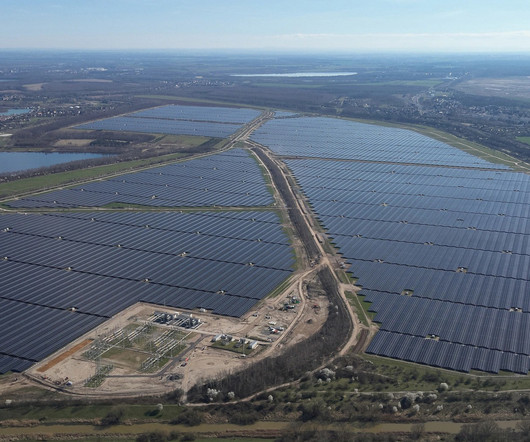
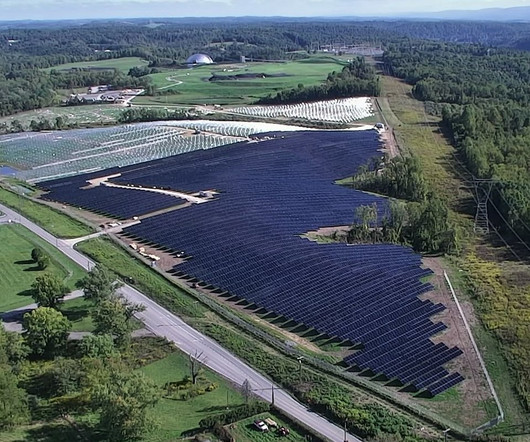
Photo: China News Service Renewable energy costs in Asia last year were 13% cheaper than coal and are expected to be 32% cheaper by 2030, according to a new study. This is significant because it marks a shift toward making renewables increasingly competitive with coal, a mainstay in APAC’s energy mix.











































Let's personalize your content