PNNL team develops electrolyte for high-voltage sodium-ion battery with extended longevity
Green Car Congress
JULY 14, 2022
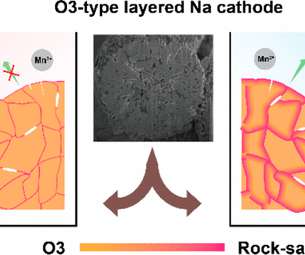
Cheap and abundant, sodium is a promising candidate for new battery technology. However, the limited performance of sodium-ion batteries has hindered large-scale application. A paper on the work appears in Nature Energy. Sodium-ion batteries (NIBs) have attracted worldwide attention for next-generation energy storage systems.


























Let's personalize your content