Study finds GHG methane offsets its warming ~30% and precipitation increase ~60% by short-wave absorption
Green Car Congress
MARCH 28, 2023
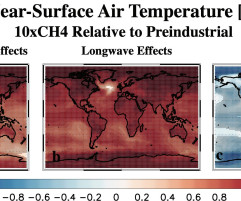
A new study by researchers from the University of California, Riverside and colleagues in the US and Europe has now found that methane short-wave absorption counteracts ~30% of the surface warming associated with its long-wave radiative effects. However, greenhouse gases also absorb short-wave radiation incoming from the sun.
























Let's personalize your content