EIA: US energy-related CO2 fell by 2.8% in 2019, slightly below 2017 levels
Green Car Congress
MAY 11, 2020
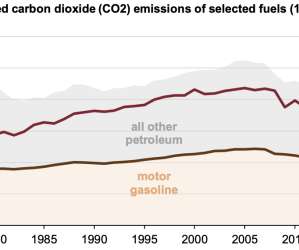
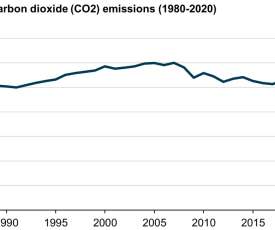
Overall, US energy-related CO 2 emissions have fallen 15% from their peak of 6,003 MMmt in 2007. CO 2 emissions from coal fell by 14.6%, the largest annual percentage drop in any fuel’s CO 2 emissions in EIA’s annual CO 2 data series dating back to 1973. The United States now emits less CO 2 from coal than from motor gasoline.






























Let's personalize your content