MIT Sequential Decomposition Synthesis process produces thin solid-state electrolytes without sintering
Green Car Congress
JUNE 12, 2022
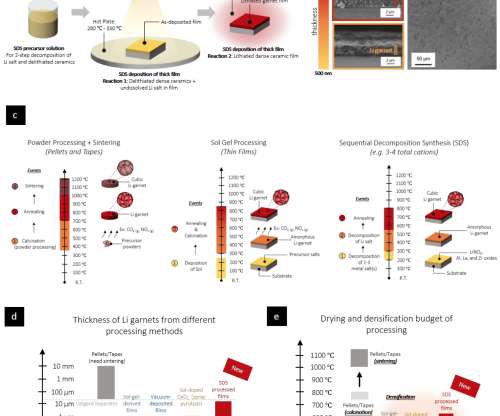
A team from MIT has developed a new approach to fabricating oxide-based solid-state electrolytes that are comparable in thickness to the polymer separators found in current Li-ion batteries without sintering: sequential decomposition synthesis (SDS). Hood et al.

























Let's personalize your content