A New Energy-Efficient Hydrogel Pulls Water From Air
Cars That Think
SEPTEMBER 21, 2023
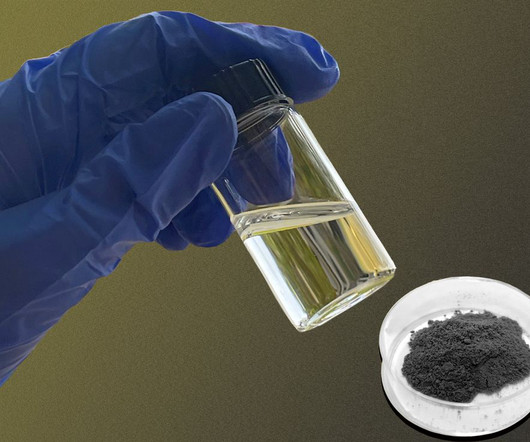
Using a new kind of hydrogel material, researchers at the University of Texas at Austin have pulled water out of thin air at temperatures low enough to be achieved with sunlight. Atmospheric water harvesting draws water from humidity in the air. The UT Austin technique is aimed at the latter.



















Let's personalize your content