UW Madison chemists discover new way to harness energy from ammonia
Green Car Congress
NOVEMBER 12, 2021
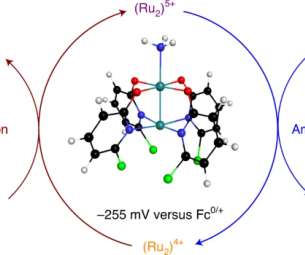
A research team at the University of Wisconsin–Madison has identified a new way to convert ammonia to nitrogen gas through a process that could be a step toward ammonia replacing carbon-based fuels. One of the drawbacks of ammonia synthesis is that the hydrogen we use to make ammonia comes from natural gas and fossil fuels. Brown, T.R.































Let's personalize your content