Cornell team develops aluminum-anode batteries with up to 10,000 cycles
Green Car Congress
APRIL 6, 2021
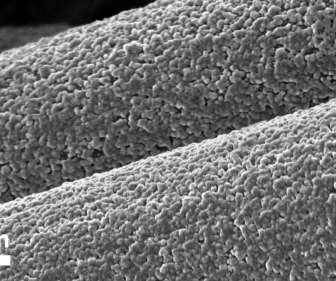
Friend Family Distinguished Professor of Engineering, have been exploring the use of low-cost materials to create rechargeable batteries that will make energy storage more affordable. These materials could also provide a safer and more environmentally friendly alternative to lithium-ion batteries.































Let's personalize your content