IEA: global CO2 emissions rebounded to their highest level in history in 2021; largely driven by China
Green Car Congress
MARCH 9, 2022
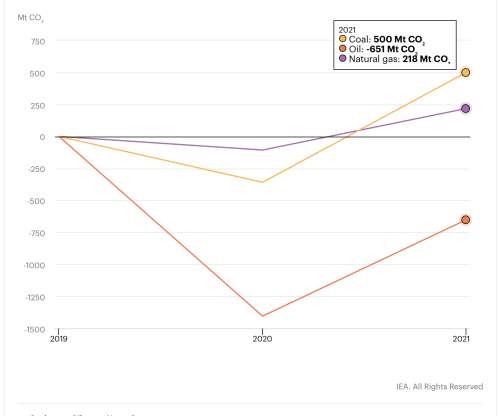
billion tonnes, their highest ever level, as the world economy rebounded strongly from the COVID-19 crisis and relied heavily on coal to power that growth, according to new IEA analysis. Coal accounted for over 40% of the overall growth in global CO 2 emissions in 2021, reaching an all-time high of 15.3 billion tonnes. billion tonnes.
















Let's personalize your content