Chevron / Toyota road trip demonstrates renewable gasoline blend
Green Car Congress
APRIL 18, 2023
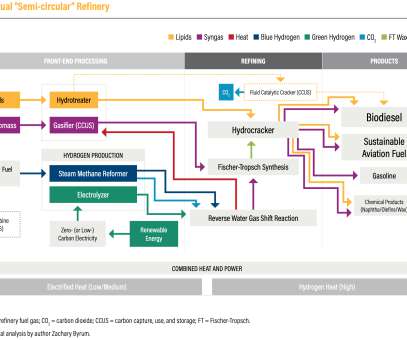
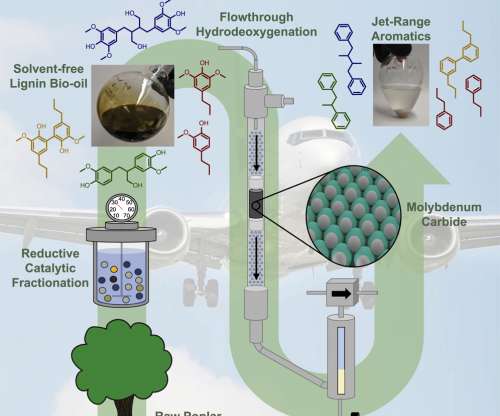
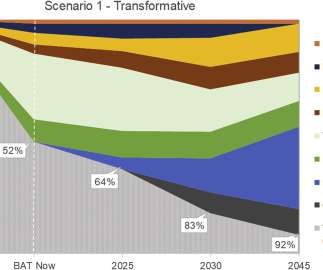
Chevron USA kicked off a road trip across the US Gulf Coast to showcase an innovative new gasoline blend with more than 50% renewable content. In February 2022, a team from Argonne National Lab published a report “Carbon Intensities of Refining Products in Petroleum Refineries with Co-Processed Biofeedstocks”.




















Let's personalize your content