Researchers investigate effect of impact on structurally-embedded Li-ion batteries
Green Car Congress
AUGUST 20, 2023
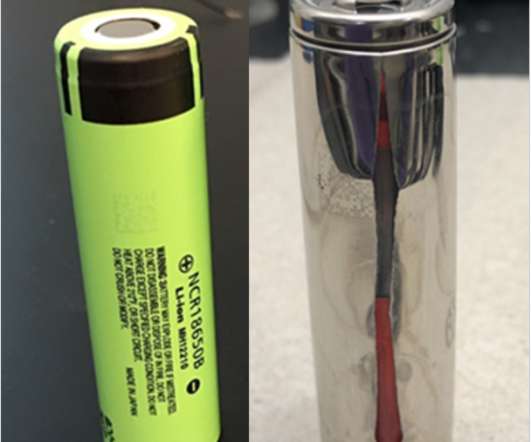
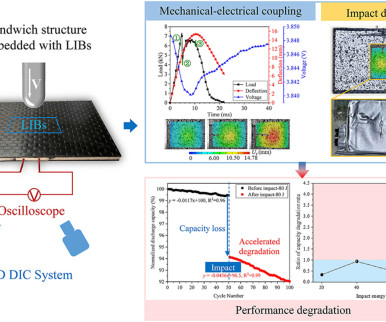
Researchers in China are investigating the effect of low-velocity impact loads on structurally embedded Li-ion batteries in vehicles. A paper on their study is published in the Journal of Power Sources. —Li et al. 2023.233509
































Let's personalize your content