TOAR shows present-day global ozone distribution and trends relevant to health; public database
Green Car Congress
FEBRUARY 6, 2018
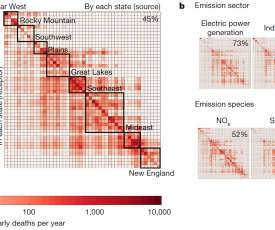
Ozone levels across much of North America and Europe dropped significantly between 2000 and 2014. People living in parts of southern Europe, South Korea and southern Japan and China also experienced more than 15 days a year of ozone levels above 70 ppb. Source: University of Leicester. Click to enlarge.















Let's personalize your content