SARI researchers propose novel method to enhance electrocatalytic conversion of CO2
Green Car Congress
SEPTEMBER 13, 2022
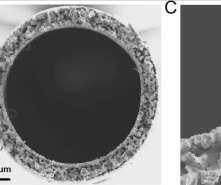
CHEN Wei and WEI Wei from the Shanghai Advanced Research Institute (SARI) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences reported a novel method that enables efficient CO 2 electroreduction to CO by virtue of low-coordination chloride ion adsorption on a silver hollow fiber (Ag HF) electrode. A) Optical image of the as-fabricated Ag HF tubes. and Sun, Y.



















Let's personalize your content