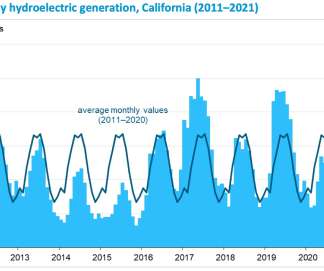
EIA: California drought will decrease hydropower, increase natural gas use and CO2 emissions
Green Car Congress
MAY 27, 2022
Figure 1 data source: US Drought Monitor , jointly produced by the National Drought Mitigation Center (NDMC) at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln, the United States Department of Agriculture, and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Graph courtesy of NDMC.













Let's personalize your content