MIT study: half of US deaths related to air pollution are linked to out-of-state emissions
Green Car Congress
FEBRUARY 15, 2020
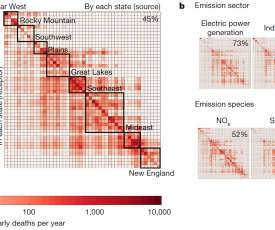
More than half of all air-quality-related early deaths in the United States are a result of emissions originating outside of the state in which those deaths occur, MIT researchers report in a paper in the journal Nature. Now it’s looking like other emissions sectors are becoming important. That wasn’t really possible before.










Let's personalize your content