Tsinghua, MIT, Argonne team discovers lithium titanate hydrates for superfast, stable cycling in Li-ion batteries
Green Car Congress
DECEMBER 17, 2017
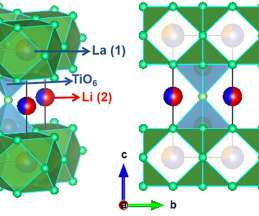
An international research team from Tsinghua University, MIT and Argonne National Laboratory has discovered a series of novel lithium titanate hydrates that show better electrochemical performances compared to all the Li 2 O–TiO 2 materials reported so far—including those after nanostructuring, doping and/or coating.













Let's personalize your content