Why Electric Buses Are the Healthy School Choice
Blink Charging
NOVEMBER 28, 2023
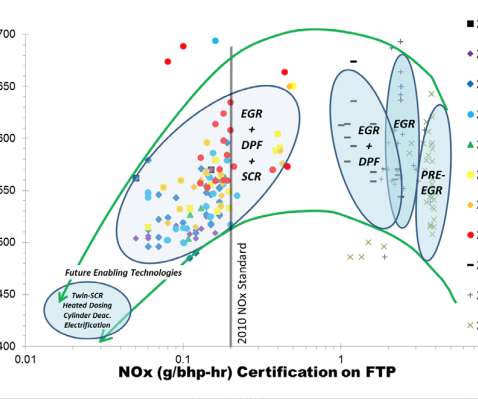
Vehicle fleets across the United States are transitioning from internal combustion engine (ICE) to electric vehicles, and that includes school bus fleets. Many school districts use diesel buses for fuel efficiency, but even diesel exhaust was classified as a known carcinogen to humans in 2012.











Let's personalize your content