Studies find global COVID-19 lockdowns have significantly reduced PM2.5 and NO2 pollution, but ozone up
Green Car Congress
MAY 12, 2020
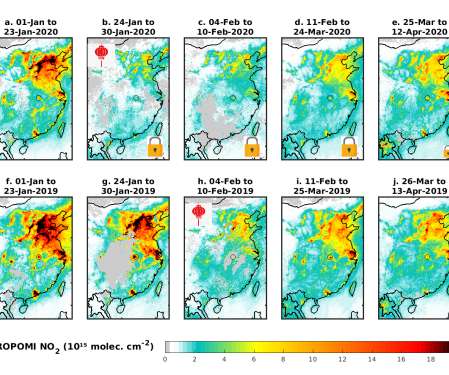
Levels of two major air pollutants have been reduced significantly since lockdowns began in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, but a secondary pollutant—ground-level ozone—has increased in China, according to new research. The week of Chinese New Year holiday is indicated by the red lantern shown inset panels (b) and (h).










Let's personalize your content