First Cobalt announces positive feasibility results for Canadian cobalt refinery expansion; first NA producer of battery-grade cobalt sulfate
Green Car Congress
MAY 6, 2020
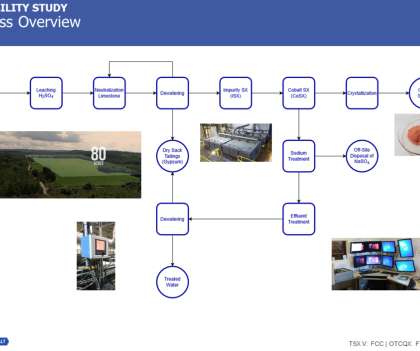
announced positive results from an independent feasibility study conducted on its permitted cobalt refinery in Ontario, Canada. Sodium Treatment. The First Cobalt Refinery is a hydrometallurgical cobalt refinery located north of Toronto, Canada. Ausenco Engineering Canada Inc. First Cobalt Corp. Capital Requirements.











Let's personalize your content