Latest GHG Inventory shows California remains below 2020 emissions target; much steeper rate of GHG reductions required
Green Car Congress
OCTOBER 23, 2020
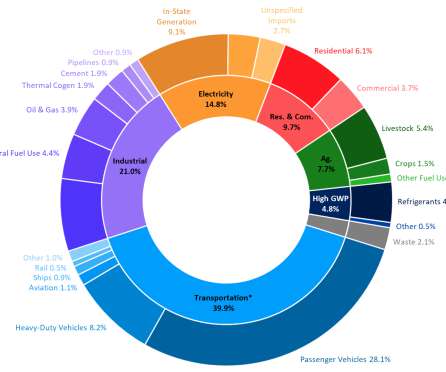
The California Air Resources Board released GHG emissions data for 2018 showing that emissions remain below 1990 levels but are effectively flat compared to 2017, while the economy grew by 4.3%. Total statewide 2018 GHG emissions were 425.3 million metric tons between 2017 and 2018, the first such decline since 2013.











Let's personalize your content