Latest GHG Inventory shows California remains below 2020 emissions target; much steeper rate of GHG reductions required
Green Car Congress
OCTOBER 23, 2020
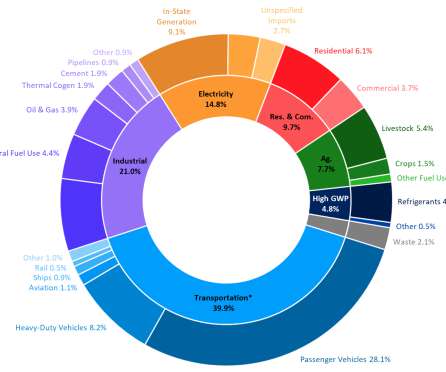
in 2018 (2000-2018 average year-over-year increase is 6.8%), continuing the increasing trend as they replace Ozone Depleting Substances (ODS) being phased out under the 1987 Montreal Protocol. Per capita GHG emissions in California have dropped from a 2001 peak of 14.0 tons per person to 10.7 tons per person in 2018, a 24% decrease.










Let's personalize your content