Cambridge researchers develop standalone device that makes formic acid from sunlight, CO2 and water
Green Car Congress
AUGUST 24, 2020
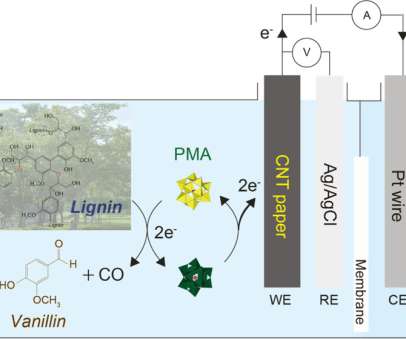
Researchers at the University of Cambridge, with colleagues at the University of Tokyo, have developed a standalone device that converts sunlight, carbon dioxide and water into formic acid, a carbon-neutral fuel, without requiring any additional components or electricity. —senior author Professor Erwin Reisner.





































Let's personalize your content