IEA: global electricity demand growing faster than renewables, driving strong increase in generation from coal
Green Car Congress
JULY 15, 2021
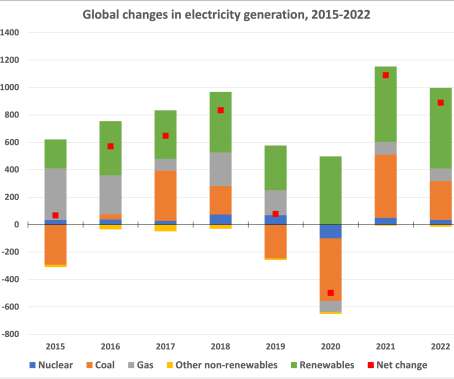
Renewables are expanding quickly but not enough to satisfy a strong rebound in global electricity demand this year, resulting in a sharp rise in the use of coal power that risks pushing carbon dioxide emissions from the electricity sector to record levels next year, according to a new report from the International Energy Agency.































Let's personalize your content