USDA study finds GHG from corn-based ethanol ~39% to 43% lower than from gasoline; reduction of >70% possible by 2022
Green Car Congress
APRIL 3, 2019
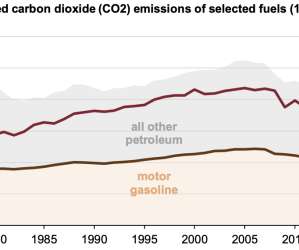
A new study released by the US Department of Agriculture (USDA) finds greenhouse gas emissions from corn-based ethanol are about 39% lower than gasoline. The study also states that when ethanol is refined at natural gas-powered refineries, the greenhouse gas emissions are even lower—around 43% below gasoline. Searchinger et al.


































Let's personalize your content