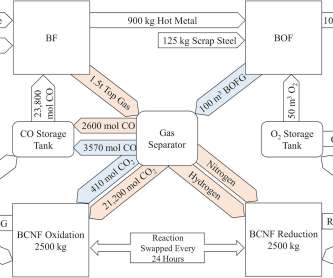
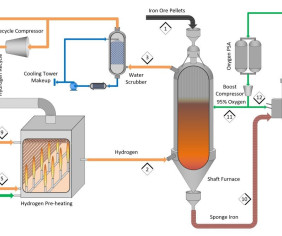
Novel adaptation for existing blast furnaces could reduce steelmaking emissions by 88%; closed-loop carbon recycling
Green Car Congress
JANUARY 26, 2023
This reduction is achieved through a closed-loop carbon recycling system, which could replace 90% of the coke typically used in current blast furnace-basic oxygen furnace systems and produces oxygen as a byproduct. If implemented in the UK alone, the system could deliver cost savings of £1.28 A double perovskite, Ba 2 Ca 0.66
































Let's personalize your content