York study: Less traffic in first UK lockdown reduced NO2 pollution but caused increase in surface ozone
Green Car Congress
DECEMBER 27, 2020
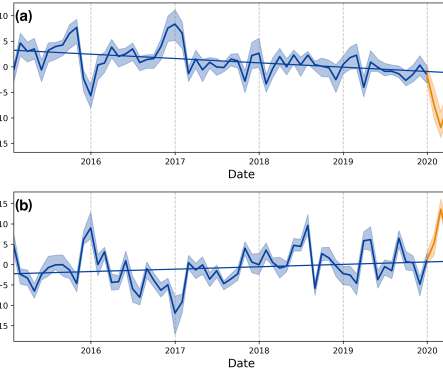
Less traffic on the roads during the first COVID-19 lockdown in the UK led to a reduction in air pollution but may have caused potentially damaging surface ozone levels to rise, according to a new study led by researchers at the University of York. The 25–75% range is shown by the shaded area. These results are a cautionary tale.

































Let's personalize your content