Who Really Invented the Rechargeable Lithium-Ion Battery?
Cars That Think
JULY 30, 2023
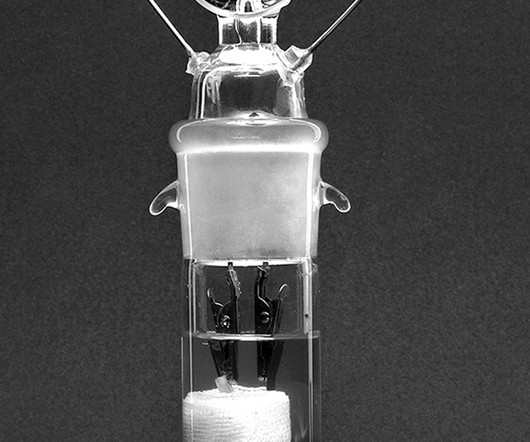
Fifty years after the birth of the rechargeable lithium-ion battery, it’s easy to see its value. Did Exxon invent the rechargeable lithium battery? Jonas Ekstromer/AFP/Getty Images In the early 1970s, Exxon scientists predicted that global oil production would peak in the year 2000 and then fall into a steady decline.




























Let's personalize your content