Sparc Hydrogen to test photocatalytic water splitting (PWS) reactor at CSIRO
Green Car Congress
JULY 3, 2023
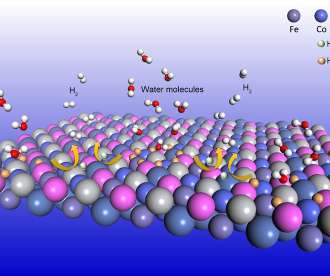
The Sparc Green Hydrogen process combines concentrated solar (CS) with photocatalytic water splitting. Prototype testing of Sparc Hydrogen’s reactor in real world conditions is the culmination of more than 5 years of research and development work conducted by the University of Adelaide and Flinders University.





































Let's personalize your content