Fraunhofer team develops process to recycle carbon black from car tires
Green Car Congress
JULY 2, 2021
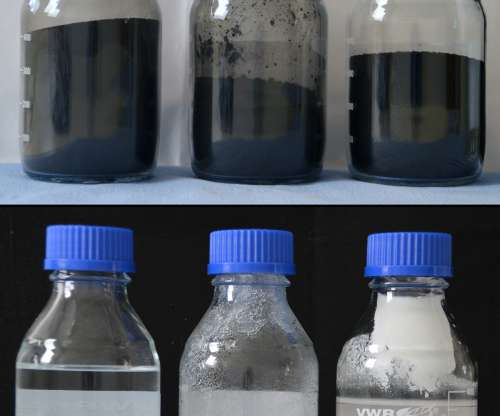
Waste tires have been used mainly for recovering energy sources; only small proportions of the carbon black contained in these tires are recycled, since mineral ash accounts for around 20% of its content. Around three kilograms of carbon black—also known as industrial soot—are found in a standard car tire. © Fraunhofer IBP.




































Let's personalize your content