Stanford engineers develop catalyst strategy to improve turnover frequencies for CO2 conversion to hydrocarbons by orders of magnitude
Green Car Congress
FEBRUARY 12, 2022
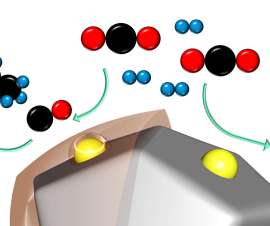
Researchers at Stanford University have shown that porous polymer encapsulation of metal-supported catalysts can drive the selectivity of CO 2 conversion to hydrocarbons. The research team encapsulated a supported Ru/TiO 2 catalyst within the polymer layers of an imine-based porous organic polymer that controls its selectivity.




































Let's personalize your content