EU project HyFlexFuel converted sewage sludge and other biomasses into kerosene by hydrothermal liquefaction (HTL); SAF
Green Car Congress
JUNE 28, 2021
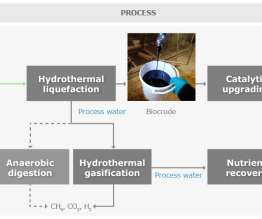
The EU-funded research project HyFlexFuel recently successfully produced biocrudes via hydrothermal liquefaction (HTL) from a variety of biomasses, including sewage sludge, food waste, manure, wheat straw, corn stover, pine sawdust, miscanthus and microalgae in a pilot-scale continuous HTL plant at Aarhus University (Denmark).


















Let's personalize your content