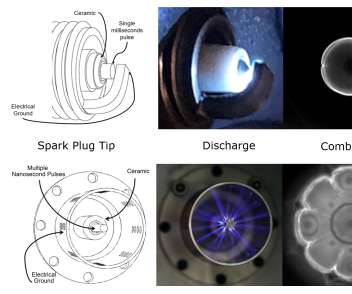
UC Riverside study finds emissions benefits for E15 blend in California
Green Car Congress
JUNE 12, 2023
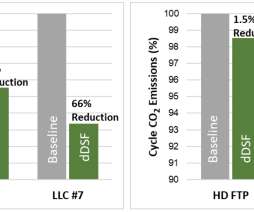
A study by a team from UC Riverside has assessed the potential of increasing ethanol content in California reformulated gasoline (CaRFG) by investigating the exhaust emissions from a fleet of 20 Tier 3 light-duty vehicles. A baseline CaRFG E10 (10% ethanol by volume) fuel was splash-blended with denatured ethanol to create an E15 fuel.































Let's personalize your content