ICCT life-cycle analysis finds no climate benefit in using LNG as marine fuel
Green Car Congress
JANUARY 29, 2020
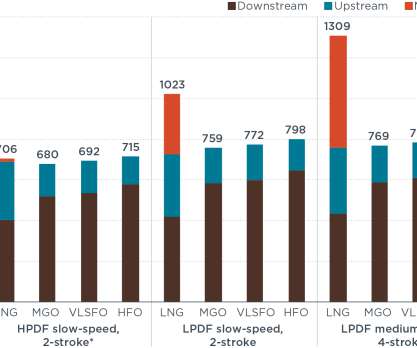
The results of a new analysis by the International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT) show that, when combined with a trend toward higher methane leakage and combustion slip, there is no climate benefit from using liquefied natural gas (LNG) as a marine fuel—regardless of the engine technology. First, it contains very little sulfur.















Let's personalize your content