New photocatalytic system converts carbon dioxide to valuable fuel more efficiently than natural photosynthesis
Green Car Congress
AUGUST 13, 2023
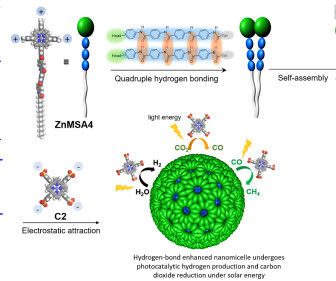
The new system mimics a natural chloroplast to convert carbon dioxide in water into methane, very efficiently using light. Photo credit: (left) Professor Ye Ruquan’s research group / City University of Hong Kong and (right) Biophysical Journal, 99:67-75, 2010. A paper on this team’s latest work was published in Nature Catalysis.


















Let's personalize your content