US DOE releases 2023 Critical Materials Assessment to evaluate supply chain security for clean energy technologies
Green Car Congress
AUGUST 1, 2023
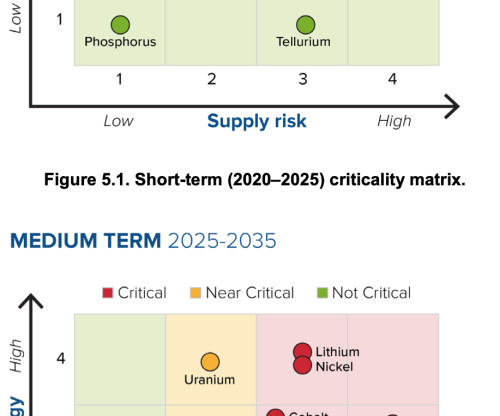
While cobalt (Co) was found to be critical in this and previous reports, lithium (Li) becomes critical in the medium term due to its broader use in various battery chemistries and the rampant growth of the EV industry. Natural graphite is a new addition in this assessment and is also found to be critical.















Let's personalize your content