Topsoe to build world’s largest SOEC electrolyzer production facility; 500 MW scalable to 5 GW; focusing on Power-to-X
Green Car Congress
MAY 24, 2022
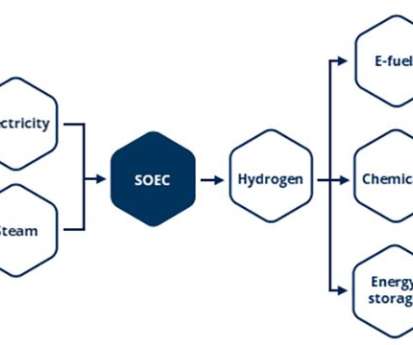
The Topsoe SOEC electrolyzer is a compact stack built primarily from abundant, low-cost ceramic materials enclosed within a metal housing. To produce hydrogen, it utilizes electricity to split water molecules (H 2 O) into hydrogen (H 2 ) and oxygen (O 2 ).










Let's personalize your content